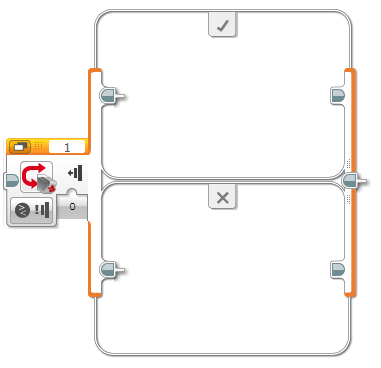
|
The Switch block is a container that can contain two or more sequences of programming blocks. Each sequence is called a Case. A test at the beginning of the Switch determines which Case will run. Only one Case will run each time the Switch is executed. |