 |
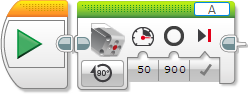
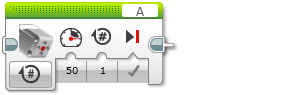
The Medium Motor block controls the Medium Motor. You can turn the motor on or off, control its power level, or turn the motor on for a specified amount of time or rotations. |
 |
The Medium Motor block controls the Medium Motor. You can turn the motor on or off, control its power level, or turn the motor on for a specified amount of time or rotations. |






| Rotations | Degrees |
|---|---|
| 1 | 360 |
| 2 | 720 |
| 0.5 | 180 |
| 1.25 | 450 |
| 7.2 | 2592 |

| Input | Type | Allowed Values | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power | Numeric | -100 to 100 | Motor power level. See Motor Power and Direction. |
| Brake at End | Logic | True/False | Applies when the block finishes. If True, the motor is stopped immediately and is held in position. If False, motor power stops and the motor is allowed to coast. |
| Seconds | Numeric | ≥ 0 | Movement time in seconds. |
| Degrees | Numeric | Any Number | Amount of movement in degrees. 360 degrees make a full rotation. |
| Rotations | Numeric | Any Number | Amount of movement in rotations. |